 4.1 学习网络编程,你应该掌握哪些 socket 函数
4.1 学习网络编程,你应该掌握哪些 socket 函数
Windows 和 Linux 上常用的 socket API 函数并不多,除了特定操作系统提供的一些基于自身系统特性的 API, 大多数 Socket API 都源于 BSD Socket (即伯克利套接字(Berkeley Sockets)),因此这些 socket 函数在不同的平台有着相似的签名和参数。
经常有想学习网络编程的新人询问要掌握哪些基础的 socket API,我这里给一个简单的函数列表,列表中给出的都是应该熟练掌握的 socket 函数。
常用 Berkeley Sockets API 一览表
| 函数名称 | 函数简单描述 | 附加说明 |
|---|---|---|
| socket | 创造某种类型的套接字 | |
| bind | 将一个 socket 绑定到一个 ip 与端口的二元组上 | |
| listen | 将一个 socket 变为侦听状态 | |
| connect | 试图建立一个 TCP 连接 | 一般用于客户端 |
| accept | 尝试接收一个连接 | 一般用于服务端 |
| send | 通过一个 socket 发送数据 | |
| recv | 通过一个socket 收取数据 | |
| select | 判断一组 socket 上的读写和异常事件 | |
| gethostbyname | 通过域名获取机器地址 | |
| close | 关闭一个套接字,回收该 socket 对应的资源 | Windows 系统中对应的是 closesocket |
| shutdown | 关闭 socket 收或发通道 | |
| setsockopt | 设置一个套接字选项 | |
| getsockopt | 获取一个套接字选项 |
对于某个 socket 函数,如果你想查看它的用法,可以通过相应的帮助文档。
# 4.1.1 Linux 系统查看 socket 函数帮助
如果是 Linux 系统,你可以通过 man 手册去查看相应的函数签名和用法。举个例子,如果你要查看 connect 函数的用法,只需要在 Linux shell 终端输入 man connect 即可。
[root@localhost ~]# man connect
CONNECT(2) Linux Programmer's Manual CONNECT(2)
NAME
connect - initiate a connection on a socket
SYNOPSIS
#include <sys/types.h> /* See NOTES */
#include <sys/socket.h>
int connect(int sockfd, const struct sockaddr *addr,
socklen_t addrlen);
DESCRIPTION
The connect() system call connects the socket referred to by the file descriptor sockfd to the address specified by addr. The addrlen argument specifies
the size of addr. The format of the address in addr is determined by the address space of the socket sockfd; see socket(2) for further details.
If the socket sockfd is of type SOCK_DGRAM then addr is the address to which datagrams are sent by default, and the only address from which datagrams are
received. If the socket is of type SOCK_STREAM or SOCK_SEQPACKET, this call attempts to make a connection to the socket that is bound to the address
specified by addr.
Generally, connection-based protocol sockets may successfully connect() only once; connectionless protocol sockets may use connect() multiple times to
change their association. Connectionless sockets may dissolve the association by connecting to an address with the sa_family member of sockaddr set to
AF_UNSPEC (supported on Linux since kernel 2.2).
RETURN VALUE
If the connection or binding succeeds, zero is returned. On error, -1 is returned, and errno is set appropriately.
ERRORS
The following are general socket errors only. There may be other domain-specific error codes.
EACCES For UNIX domain sockets, which are identified by pathname: Write permission is denied on the socket file, or search permission is denied for one
of the directories in the path prefix. (See also path_resolution(7).)
EACCES, EPERM
The user tried to connect to a broadcast address without having the socket broadcast flag enabled or the connection request failed because of a
local firewall rule.
EADDRINUSE
Local address is already in use.
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
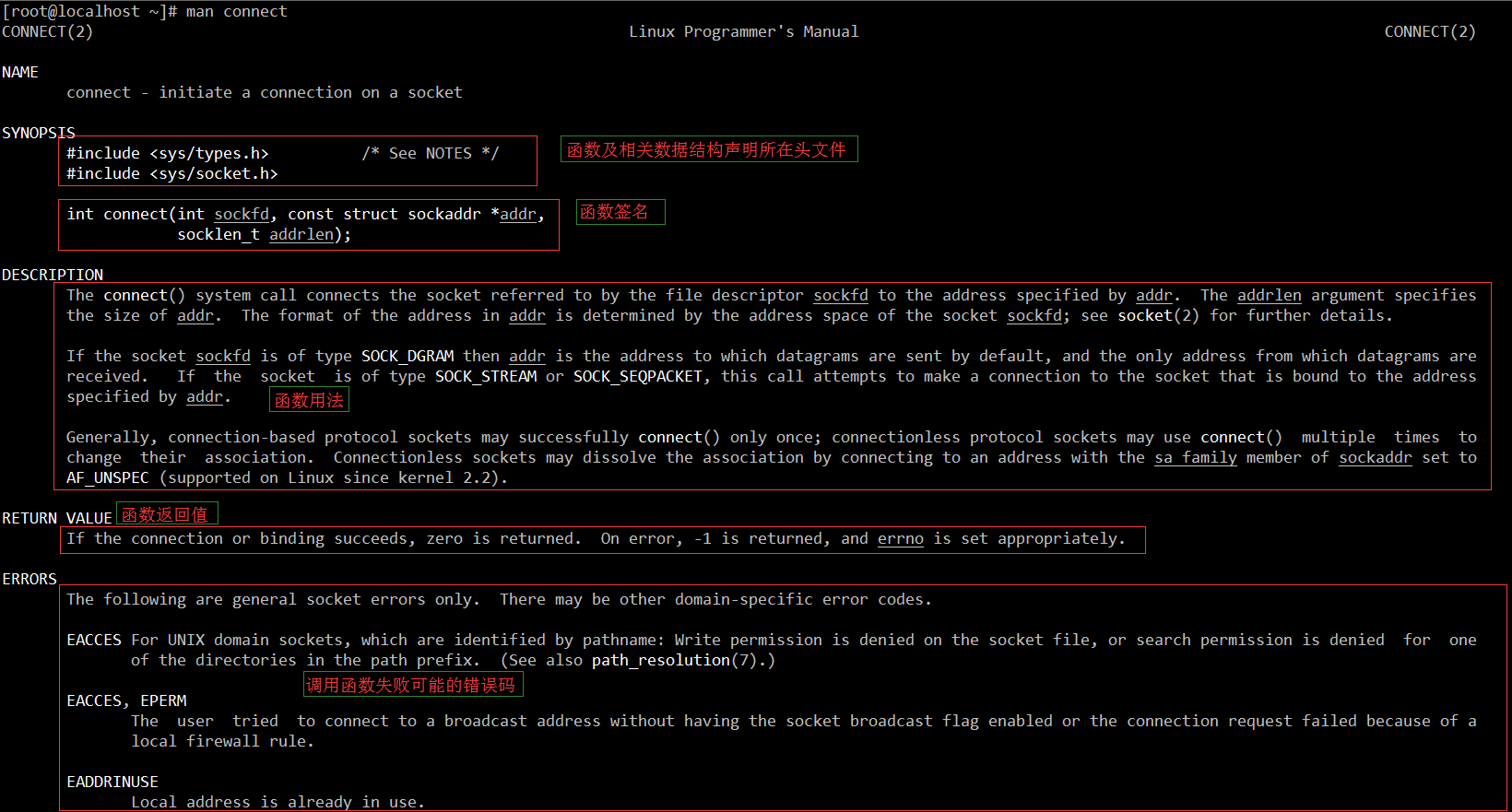
如上面的代码片段所示,man手册对于一个函数的说明一般包括如下几部分:
- 函数声明及相关数据结构所在的头文件,你实际编码时如果需要使用这个函数必须包含该头文件;
- 函数的签名,即该函数的参数类型、个数和返回值;
- 函数用法说明,并可能包括一些注意事项;
- 函数返回值说明;
- 调用函数出错可能得到的错误码值;
- 一些相关函数在 man 手册的位置索引。(connect 没有这个部分)
如下图所示:
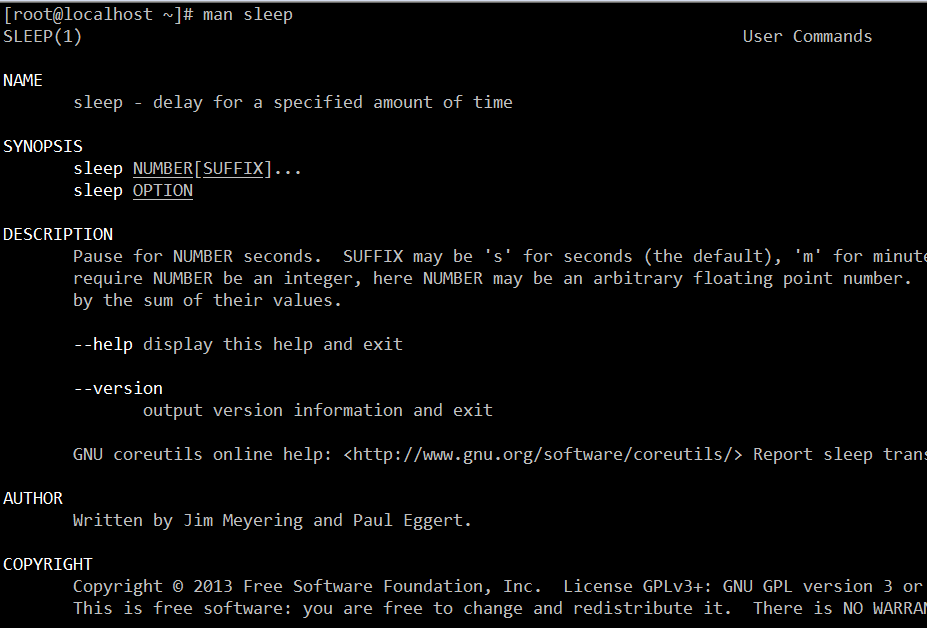
需要注意的是,这个方法不仅可以查 socket 函数也可以查看 Linux 下其他通用函数(如 fread)甚至一个 shell 命令(如 sleep)。以 sleep 为例,如果你想查程序中 sleep 函数的用法,由于Linux 内置有一个叫 sleep 的 shell 命令,如果你在 shell 窗口直接输入 man sleep,显示出来的默认会是 sleep 命令而不是我们要的 sleep 函数的帮助信息。
我们可以通过 man man 命令查看一下 man 手册组成部分:
[root@localhost ~]# man man
## 无关的部分,省略...
The table below shows the section numbers of the manual followed by the types of pages they contain.
1 Executable programs or shell commands
2 System calls (functions provided by the kernel)
3 Library calls (functions within program libraries)
4 Special files (usually found in /dev)
5 File formats and conventions eg /etc/passwd
6 Games
7 Miscellaneous (including macro packages and conventions), e.g. man(7), groff(7)
8 System administration commands (usually only for root)
9 Kernel routines [Non standard]
A manual page consists of several sections.
通过上面的代码片段,我们可以看出来,man 手册的内容总共有9部分组成,而 sleep 函数属于上面的 Section 3,所以我们输入 man 3 sleep 就可以查看 sleep 函数的帮助信息了:
[root@localhost ~]# man 3 sleep
SLEEP(3) Linux Programmer's Manual SLEEP(3)
NAME
sleep - sleep for the specified number of seconds
SYNOPSIS
#include <unistd.h>
unsigned int sleep(unsigned int seconds);
DESCRIPTION
sleep() makes the calling thread sleep until seconds seconds have elapsed or a signal arrives which is not ignored.
RETURN VALUE
Zero if the requested time has elapsed, or the number of seconds left to sleep, if the call was interrupted by a signal handler.
CONFORMING TO
POSIX.1-2001.
BUGS
sleep() may be implemented using SIGALRM; mixing calls to alarm(2) and sleep() is a bad idea.
Using longjmp(3) from a signal handler or modifying the handling of SIGALRM while sleeping will cause undefined results.
SEE ALSO
alarm(2), nanosleep(2), signal(2), signal(7)
COLOPHON
This page is part of release 3.53 of the Linux man-pages project. A description of the project, and information about reporting bugs, can be found at
http://www.kernel.org/doc/man-pages/.
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
# 4.1.2 Windows 上查看 socket 函数帮助
Windows 也有类似 man 手册的帮助文档,早些年 Visual Studio 会自带一套离线的 MSDN 文档库,其优点就是不需要电脑联网,缺点是占磁盘空间比较大,内容陈旧。在手机网络都如此普及的今天,笔者还是建议使用在线版本的 MSDN。查看 Windows API 的帮助链接是:https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/desktop/,在页面的搜索框中输入你想要搜索的 API 函数即可。
需要注意的是,建议读者在页面的底部将页面语言设置成English,这样搜索出来的内容会更准确更丰富。如下图所示:
我们还是以 connect 函数为例,在上述页面的搜索框中输入 socket connect ,然后回车,得到一组搜索结果,我们选择我们需要的页面,打开链接:https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/desktop/api/winsock2/nf-winsock2-connect。与简陋的 man 手册相比,MSDN 关于connect 函数的说明就比较详细了,大体也分为以下几部分:
- Syntax, 即函数签名,函数的参数类型、个数和返回值;
- Parameters,参数的用法详细说明;
- Return Value, 函数的返回值说明,在返回值部分,还有如果函数调用失败详细的错误码说明信息;
- Remarks,这部分就是该函数的详细用法说明,某些函数还会给出示例代码;
- Requirements,这部分指的是要使用这个函数,操作系统的版本要求,代码需要引入的头文件和库文件(如果有的话)。
- See Also, 这部分一般是一些相关函数和知识点的链接信息。
需要注意的是,在 MSDN 上阅读相关 API 的帮助信息时,你要辩证性地对待其提供的信息,因为很多函数的实际工作原理和行为并不一定如 MSDN 介绍的那样。所以在有些 API 帮助下面会有一些读者的评论信息,这些评论信息或对文档内容做一些补充或纠错,或给出一些代码示例。建议读者实际查阅时,留意一下这部分信息,或许能得到一些很有用的帮助。
本专题的目的不是逐一介绍每个 socket 函数的基本用法,因为已经有大量的网络编程书籍介绍过了,重复没有意义。当然,这并不是说明它们不重要,相反读者应该认真地把每一个函数的用法都学会。本专栏的重点是介绍网络编程中关于上述socket函数的一些重要使用事项和原理,让我们从下一节正式开始。
